Business Analysis techniques Series – Vendor Assessment assesses ability of a potential vendor to meet commitments with respect to delivery and consistent provision of a product or service. Ensure that supplier is financially secure, capable of maintaining specific staffing levels, committing appropriately skilled staff to support solutions, etc. NFRs can be used to define service levels (SLAs) expected of a third party.
Assess vendors formally using Request for Information (RFI), Request for Quote (RFQ), Request for Tender (RFT), or Request for Proposal (RFP).
RFI: Intent is to get information. Open to multiple solutions.
RFP: Intent is to get a proposal when scope is understood.
RFQ: Solution is defined. To get the price.
RFT: Has legal mandate.
Steps for vendor assessment
Determine knowledge, and expertise to be transferred, and method of execution. Consider vendors to provide knowledge, and expertise not internally available. Check out the Business Analyst article here.
Choose licensing and pricing models
Solutions with similar functionalities may differ greatly in licensing models. Analyze different usage scenarios to determine which option will provide best benefit to cost ratio. Determine product reputation and market position. Compare each vendor with competitors and decide with which player organization wants to get involved.
Determine terms and conditions
Determine if services provided by a vendor are temporary or permanent. Consider challenges in vendor’s licensing terms, and technology while transitioning to another vendor. Consider vendor’s business analysts use of, and responsibility for protecting integrity of organization’s confidential data, and customization terms for product.
Determine vendor reputation
Vendor’s experiences with other customers provide valuable information on how likely the vendor will be able to meet its contractual, and non-contractual obligations. Evaluate vendors for conformance, and compliance with external relevant standards for quality, security, and professionalism.
Determine vendor stability
Determine vendor’s ability to provide required services in future. Mitigate risks with respect to vendor financial difficulties. Ensure to maintain and enhance solutions even if the vendor’s situation changes radically.
Strengths
- Ensures vendor is reliable and organization expectations are met.
- Reduces risk of choosing an unsuitable vendor.
- Improved long-term satisfaction with decision.
Limitations
- Time-consuming to gather sufficient information on multiple vendors.
- Risk of failure as partnership evolves cannot be prevented.
- Subjectivity may bias evaluation outcome.
Example:
Let us learn the process model by means of an example. Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) management system is developed for the IT and ITES domain. The primary objective of GRC management system is to help companies implement Governance, Quality, and Information Security Management Systems in an integrated manner. It has various features, one of which is to plan and track projects and programs using standards such as CMMI, ISO 9001, and ISO 27001 etc.
Through this example let us try to understand how ABCT would like to hire an IT firm to provide 24 by 7 user support for the Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC) management system.
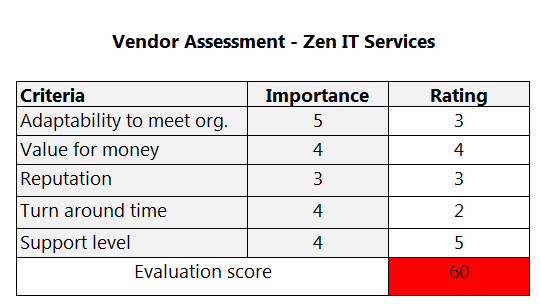
ABCT has put an over score of 70% for vendor to be considered as suitable vendor.
Here is the Vendor Assessment report for Zen IT Services.
Read more: What Social Media Management Agencies Can Do for Your Business

