Last Updated on March 24, 2024 by Nasir Hanif
Honeypots are security tools that a website can place on its server. They can be used for different purposes. Some are used to monitor traffic, while others are used to detect malicious websites. There are different kinds of honeypots: low-interaction, medium-interaction, and virtual honeypots. The type of malware honeypot you need depends on the security threat you’re trying to prevent.
Low-Interaction Honeypots
Honeypots can be built to increase security and minimize attack surfaces. Low-interaction honeypots can be built with limited resources and require little management effort. They can be used to monitor network-based threats, track malware propagation, study internet-wide threats, and provide real-time alerts of highly automated attacks.
High-interaction honeypots may be more appropriate for observing attackers inside the target system. These honeypots may capture activities from different attackers, including worms and automatic software. Identifying these patterns allows honeypots better to understand the intent of attackers and their goals. These honeypots also can help detect the behavior of attackers who create botnets.
Low-interaction honeypots can be deployed to test the effectiveness of network defense and can detect attacks without exposing full operating system functionality. Honeypots have been around for about 15 years. Therefore, it is important to understand their limitations and how they work before deploying them on your system. Honeypots can be a powerful tool to detect sophisticated attacks, but their limitations must be carefully considered.
Medium-Interaction Honeypots
Medium-interaction honeypots increase security by mimicking software to fool an attacker into thinking they’re accessing an existing system. These honeypots may take more time to set up and require more specialized knowledge. This level of sophistication makes them more convincing to threat actors.
Honeypots are a great way to monitor attacks. These devices simulate an actual target network and can be used by businesses, researchers, and consumers to gather information on hackers. The data they collect can help network administrators strengthen their cybersecurity strategy. Honeypots can be used to detect attacks on large enterprise networks, as well as to monitor the activity of malicious users.
Medium-interaction honeypots differ from low-interaction honeypots because they can emulate more of an attacker’s actions. These devices don’t have their operating system, but they offer more services than low-interaction honeypots. These honeypots are expensive and difficult to implement, but they can provide extensive information about hackers.
High-interaction honeypots are more realistic looking. They imitate production systems and allow attackers to do some actual activities. As a result, the attackers are unlikely to realize they’re being observed. Since high-interaction honeypots imitate real systems, they are more effective in revealing attacks and tactics.
Virtual Honeypots
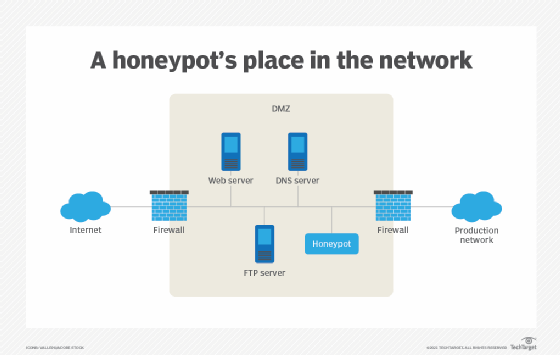
Virtual honeypots increase security and compliance by making it more difficult for attackers to compromise a system. They can be deployed in several ways, including as an ad hoc response to active security threats, as a way to understand attack methods, and as a way to divert hackers from attacking legitimate systems. There are two main types of honeypots: research and production. Research honeypots are placed in an external network to study attack methods, while production honeypots are placed inside an organization’s internal network. These are typically smaller and simpler than research honeypots. They detect active attacks on the organization’s internal network and divert hackers from attacking legitimate servers.
In addition to increasing security, virtual honeypots may be used for commercial purposes. In the case of commercial users, honeypots may be used to prove a point or to influence an attacker to commit a crime. How you use honeypots depends on the type of information you plan to collect. For example, if you intend to use your honeypot for business purposes, you must ensure that you follow all the legal requirements in your country.
Apart from thta if you want to know about 5 Biggest Cyber Security Threats then please visit our business page